The rapidly growing technological landscape has led to increased production of electronic materials. Today, an increasing number of people are shopping for electronic products. In fact, the global unit sales of smart devices skyrocketed and hit the 60 million mark from 2013 to 2022.
The launch of new electronic gadgets encourages people to try them out. This means that the now antiquated models are often discarded. The outdated electronic equipment that individuals aim to discard is referred to as e-waste. But why does that matter? Keep reading to find out everything you need to know about e-waste, including what it is, what causes it, and how to manage it.
What Is Electronic Waste (E-Waste)?
Electronic waste/E-waste refers to any electrical equipment that has been discarded. This includes both working and damaged items that are discarded or donated to a charity reseller. Suppose the item isn't sold; it will be discarded. Basically, e-waste is generated when an electronic product is discarded after the end of its useful life.
E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams. According to a recent survey, around 63.3 million tons of electronic waste was generated globally in 2021, with China contributing the highest portion. That said, e-waste constitutes around 8% of municipal solid waste streams in rich countries like those in the GCC. Globally, electronic waste constitutes over 5% of all municipal solid waste streams and is growing with the increase in sales of electronic products in developing countries. The United States alone generated 6.92 million tons of e-waste, or about 46 pounds per person.
The largest constituents of electronic waste are iron and steel, accounting for approximately 50%. They are followed by plastics which account for 21%. Non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper and precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium account for 13% of e-waste. Additionally, e-waste contains toxic elements such as cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury, and selenium. Arsenic is the only toxic substance that you can't find in the e-waste.
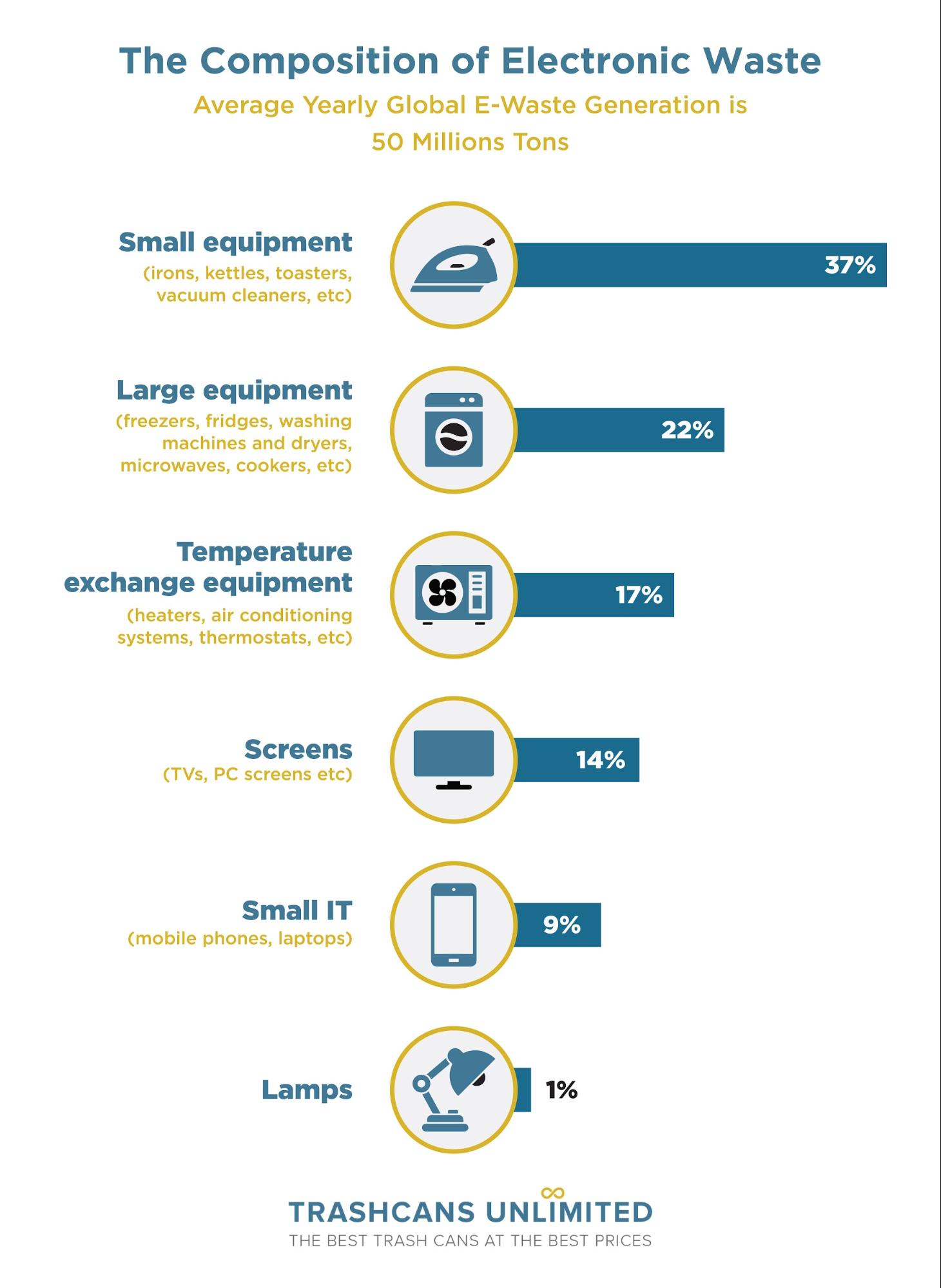
Typical electronic waste devices include but are not limited to:
- Communication and information technology devices such as smartphones, cell phones, desktop computers, laptops, hard drives, and circuit boards
- Small appliances such as toasters, microwaves, vacuums, hair dryers, power tools, fans, and heaters
- Large appliances such as refrigerators, dishwasher, washing machine, refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners
- Home entertainment devices such as PCs, DVDs, VCRs, Blu-ray players, video game systems, televisions, and radios
- Electronic utilities such as lamps, light bulbs, batteries, heating pads, electric cords, treadmills, and smartwatches
- Office and medical equipment such as copiers, printers, imaging equipment, IT servers, network hardware, and audio & video equipment
What Causes Electronic Waste?
The rapidly growing technological landscape has led to increased production of electronic materials. The main cause of e-waste is the rising demand for electronic products.
Often, when electrical appliances break, consumers opt to purchase a replacement, more so if it is more economical than fixing the broken one. In other scenarios, the annual launch of new electronic gadgets encourages people to upgrade annually. This means that the now antiquated models are often discarded. The outdated electronic equipment that individuals aim to discard is referred to as e-waste.
That said, there are two factors that make e-waste a growing environmental concern.
- First, e-waste contains dangerous chemicals that, when broken down in landfills, tend to leak hazardous substances into the air and soil, creating an unhealthy environment.
- Second, electronic waste takes much longer to decompose, so the toxic substances are present for longer durations.
Why Is Electronic Waste Hazardous?
As mentioned earlier, electronic waste contains harmful chemicals. This is one of the reasons it is more expensive and difficult to process, and why e-waste is a growing concern for Universities increasing recycling efforts. When electronic waste is dumped on a landfill site for an extended duration, the chemicals begin to leach the soil, air, and waterways, thereby posing a threat to animals, humans, plants, and the environment as a whole.
E-Waste Effects on Air
Air contamination occurs when electronic waste is informally disposed of by burning, dismantling, melting, or shredding the materials, thereby releasing dust particles and toxins like dioxins into the environment. These substances can damage respiratory health and cause chronic diseases and cancer. The negative effects of air pollution are not limited to human beings only; they can also affect plants and animals.
E-Waste Effects on Soil
When e-waste is improperly disposed of in regular landfills or illegal dumpsites, flame redundant and heavy metals can seep into the soil, contaminating the underlying groundwater. Consequently, the water will contaminate the crops that will be planted in that location in the future. Crops grown in contaminated soil are vulnerable to absorbing toxins that can cause many illnesses and diminish the productivity of farmland.
E-Waste Effects on Water
When heavy metals from electronic waste reach the groundwater, they eventually make their way to streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes. Through these pathways, the water becomes acidified and toxified, making it unsafe for plants, animals, and even communities that live a couple of miles away from the recycling site. The acidification of water can kill freshwater and marine organisms, disrupt biodiversity and harm the ecosystem.
What Should I Do With My Electronic Waste?
Suppose you have some electronic waste that you want to dispose of; there are safe ways of doing so. Here are some of the actions you should take:
1. Recycle
The best way to curb the negative effects of e-waste is to recycle electronic products. Remember, electronic waste contains recyclable materials such as glass, plastic, copper, gold, silver, and platinum, which are valued at $57 billion. Even so, most are either burnt or dumped instead of being collected for recycling. In fact, it is estimated that while precious metals are worth around $14 billion, only $4 billion is recovered at the moment. This means that around $10 billion goes to waste.
While e-waste is recyclable, you can’t simply throw it in the same recycling bins with cans and paper. Manufacturers, retailers, and other programs offer options to recycle electronics, such as mailing or dropping electronics at a specified location. Make sure you’re storing and sorting your recyclables correctly with the right recycling containers from Trashcans Unlimited. We even have helpful resources to help you start an office recycling program.
2. Check If It Can Be Fixed
Before deciding to dispose of your electronic devices, you should check whether they can be fixed by taking them to a repair shop. This could save you a lot of money and help the environment at the same time.
3. Donate to Charity
In case you've decided that it's time to upgrade, and your electronic device is still in good working condition, donating it to charity would be a noble cause. While the device may not be valuable to you, it could change someone else's life positively.
4. Exchange Your Old Appliance
Retailers like Samsung and CEX offer a product exchange service as part of their environmental sustainability initiatives. This means that you can exchange your old devices for a newer model. Retailers and manufacturers who participate in such initiatives ensure that older electronic devices are disposed of safely and properly.
5. Sell Your Device
Again, suppose your device is in good working condition; you could earn extra money selling it on platforms such as eBay or Facebook Marketplace.
Trashcans Unlimited for E-Waste Recycling & Waste Management
Electronic waste is a big challenge for governments, organizations, and institutions around the globe. It is becoming a significant public health problem as it's exponentially growing by the day. To effectively manage the recycling and disposal of waste, there's a need to integrate the formal sector with the informal sector and establish mechanisms for safely handling and treating electronic waste.
Are you looking for recycling bins for waste recycling and management? Trashcans Unlimited can help. We offer a wide variety of trash cans and recycling bins to fit your needs. Start browsing our selection of high-quality trash cans, or contact us today with questions.

