The fruit fly life cycle is a fascinating process that involves several stages of development. Understanding this life cycle is crucial for various reasons, including scientific research, genetic studies, and agricultural practices.
In this article, we will explore the different stages of a fruit fly's life and examine the factors that influence its development. We will also cover the intricate world of fruit flies and uncover the timeline of their life cycle.
But before we delve into the specifics, let's first understand why studying the fruit fly life cycle is so important. First things first, what is a fruit fly?
What is a Fruit Fly?
Fruit flies, scientifically known as Drosophila Melanogaster, have become a model organism for numerous biological studies. They are tiny insects, measuring about 3 to 4 millimeters in length, with reddish-brown bodies and bright red eyes, making them easily recognizable.
Feeding Habits
These tiny creatures have a keen sense of smell, which helps them locate food sources from a distance. They are attracted to ripe fruits and vegetables, which serve as their primary food source. The ability to quickly locate and infest ripened produce has made fruit flies a significant agricultural pest.
Reproductive Habits
When it comes to reproduction, fruit flies exhibit a unique behavior known as "mating swarms." Which is when males gather in groups and perform elaborate courtship dances including wing vibrations, pheromone release, and specific body movements to attract females.
Once a female fruit fly mates, she stores the sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca, which allows her to fertilize her eggs over an extended period. The female then lays her eggs, thus beginning their life cycle.
By studying the fruit fly life cycle, scientists gain valuable insights into various biological processes, including cellular development, aging, genetic pathways, and disease progression. So let’s take a look at why they are used for scientific research.
The Importance of Studying the Fruit Fly’s Life Cycle
One may wonder why fruit flies deserve such attention in the field of biology. Surprisingly, fruit flies share a significant portion of their genetic material with humans, making them an invaluable resource for understanding our own biology. So let’s look at some reasons of why they are so valuable for scientific research:
- They reproduce rapidly, allowing researchers to observe multiple generations in a short period of time.
- They aid in the study of heritability and genetic variation.
- They allow scientists to determine how specific genes are passed on from generation to generation.
- They have a relatively short life span, which allows researchers to quickly gather data.
- Their tiny bodies make it easier to handle and manipulate them in laboratory settings.
Furthermore, researchers can easily control environmental factors and introduce specific genetic modifications to study the effects on the fruit fly's life cycle. Now let’s get into more detail about how the fruit fly’s life cycle works.
The 4 Main Stages of a Fruit Fly's Life
Like many other insects, the fruit fly undergoes a complete metamorphosis, meaning it goes through four distinct stages of development. Each of these stages is unique and plays a vital role in the fruit fly's life cycle. So let’s look at each with a little more detail.
| The Stage | What Happens |
| The Egg Stage | Female fruit flies lay up to 500 eggs, which are deposited in organic matter, providing a suitable environment including temperature, humidity, and availability of food, which can impact the survival rate of the eggs. |
| The Larval Stage | The larvae, also called maggots, undergo several molting stages and start feeding on their surrounding food source, like rotting fruits for approximately five days to prepare for their next transition. |
| The Pupal Stage | During this stage, their organs are rearranged and reshaped within a protective shell called a puparium, transforming them into the recognizable form of an adult fruit fly. |
| The Adult Stage | At this point, the fly has fully functional wings and reproductive organs and it’s ready to mate and continue the life cycle. |
By studying the behavior and reproductive patterns of these creatures, researchers can develop effective strategies to control fruit fly infestations and minimize their impact on agriculture and human health. But how long exactly does this fascinating cycle last?
A Detailed Timeline of a Fruit Fly's Life Cycle
Now that we've examined the different stages of a fruit fly's life cycle, let's take a closer look at the timeline of their development and break it down further step-by-step.
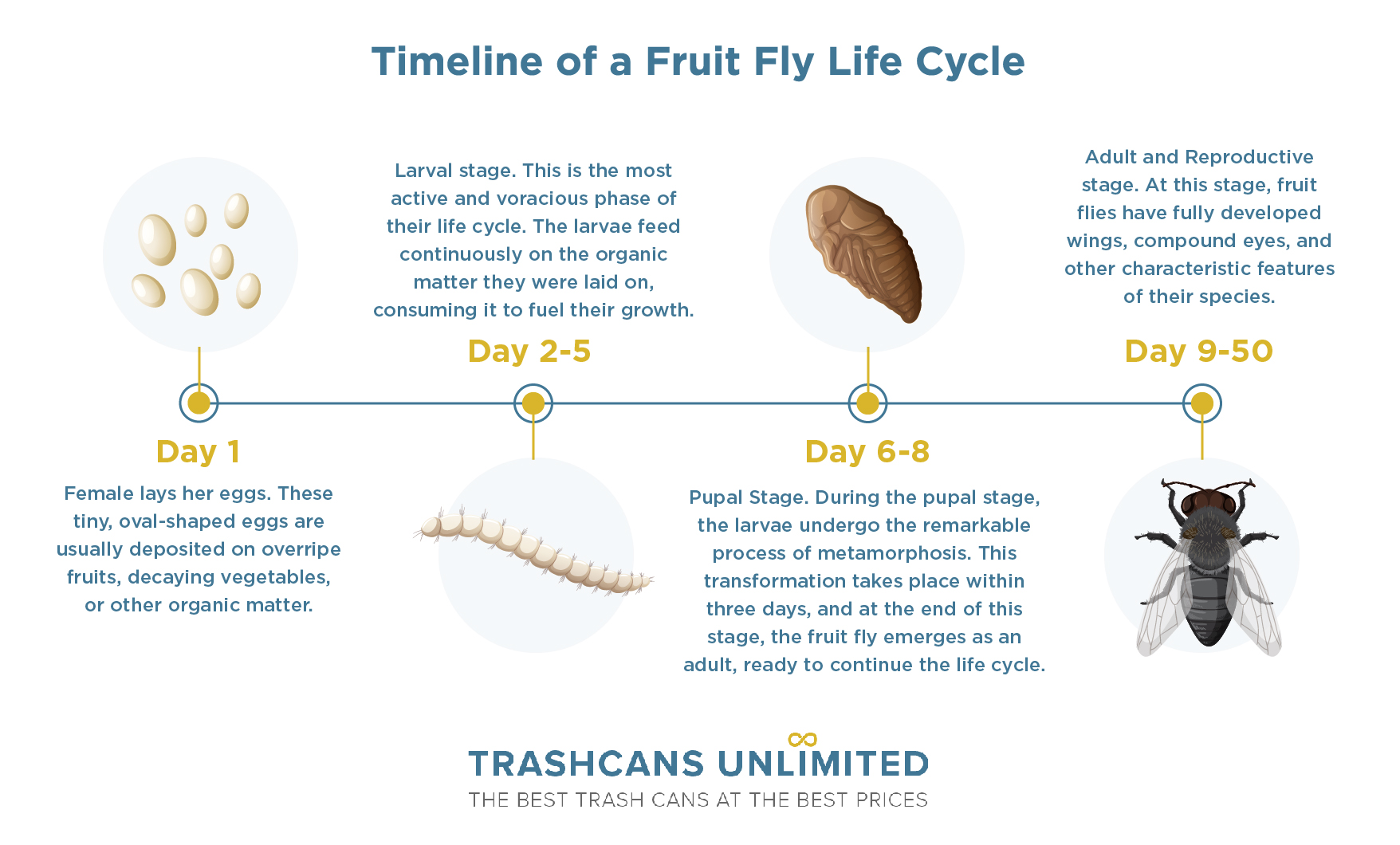
Day 1 | Egg Laying
The start of the fruit fly's life cycle begins with the female laying her eggs. These tiny, oval-shaped eggs are usually deposited on overripe fruits, decaying vegetables, or other organic matter that serves as a suitable food source for the developing larvae.
Days 2–5 | Larval Development
Within 24 hours, these eggs hatch, and the larvae, which at this point measure 1 millimeter in length and are almost transparent, emerge. During the next four days, the larvae enter the larval stage, which is the most active and voracious phase of their life cycle.
The larvae feed continuously on the organic matter they were laid on, breaking it down and consuming it to fuel their growth. As they grow, the larvae undergo several molts, shedding their exoskeletons and increasing in size, allowing them to become more robust and better equipped to survive.
Days 6–8 | Pupal Stage
During the pupal stage, the larvae undergo the remarkable process of metamorphosis inside their protective pupal case. During the span of three days, their organs, muscles, and other structures are broken down and rebuilt to form the adult fruit fly.
Days 9–50 | Adult Life and Reproduction
At this stage, they have fully developed wings, compound eyes, and are now capable of reproducing and will continue to do so for a period of about 30 to 50 days, depending on various factors such as environmental conditions and available resources.
During their adult lives, fruit flies play a crucial role in pollination and the decomposition of organic matter. They are attracted to fermenting fruits and vegetables, where they lay their eggs and continue the life cycle.
Overall, the life cycle of a fruit fly is a remarkable example of nature's efficiency and adaptability. However, there are a few factors that determine their survival. So, let’s get into the factors that determine the fruit fly’s life cycle.
The 4 Factors That Determine The Fruit Fly’s Life Cycle
While the general timeline for a fruit fly's life cycle remains relatively consistent, various external factors can influence its duration and development. Let's explore some of these influential factors:
Temperature
Fruit flies are ectothermic organisms, meaning their body temperature is regulated by the environment. Warmer temperatures accelerate their development given their metabolic rate increases, whereas cooler temperatures prolong the process.
Humidity
In addition to temperature, humidity also plays a vital role in fruit fly development. Higher humidity levels promote egg hatching and larval growth given the moisture in the environment provides the necessary conditions for fruit fly eggs to hatch and larvae to thrive.
Availability of Food
Fruit flies are attracted to ripe fruits and organic matter, which serve as their primary sources of nutrition. When there is an abundance of suitable food sources, fruit flies experience faster growth and development given they enable them to undergo metamorphosis more efficiently.
On the other hand, when fruit flies face a lack of food, they enter a state of diapause, a period of suspended development where the fruit fly's metabolic activity decreases, allowing it to conserve energy until food becomes available again.
This adaptive mechanism helps fruit flies survive in challenging environments and ensures their life cycle can resume once favorable conditions return. Making them one of the hardest infestations to eradicate.
Presence of predators
The small size and abundance of fruit flies make them attractive prey for various predators such as birds, spiders, and other insects that can disrupt or shorten the fruit fly's life cycle. This is because the constant threat of predation forces fruit flies to allocate more energy towards evasive behaviors, reducing the time and resources available for growth and reproduction.
However, it is worth noting that the presence of predators can also have evolutionary benefits for fruit flies. Over time, this can lead to the emergence of fruit fly populations with increased resistance or avoidance strategies, ultimately shaping their life cycle dynamics.
Practical Applications for Understanding the Fruit Fly’s Life Cycle
Now that we have examined the intricacies of the fruit fly life cycle, let's explore some practical applications of this knowledge so we can better understand how much these tiny creatures can impact our understanding of agriculture, genetic research, and scientific studies.
| Field | Applications |
| Agriculture | By understanding the factors that determine their growth and reproduction, such as temperature and humidity requirements, farmers can implement targeted interventions, like adjusting irrigation or using protective netting, to reduce fruit fly populations and protect their crops. |
| Genetic Research | The fruit fly's short lifespan and simple genetics make it an ideal model organism for genetic studies, which allow researchers to advance our understanding of human genetics and diseases by gaining insights into gene expression, heritability, and genetic variation. |
| Cancer Research | Fruit flies can be genetically modified to mimic certain aspects of human cancers, allowing scientists to test potential treatments and has led to the discovery of genes and pathways that play a role in cancer development. |
| Biology | By manipulating the fruit fly genome, researchers can study how specific genes contribute to the formation of various tissues and organs, which will potentially lead to breakthroughs in the treatment of birth defects and organ damage. |
The Fascinating Life of Fruit Flies
Throughout their brief lifespan, fruit flies play a significant role in scientific research and agricultural practices. As we continue to uncover the complexities of the fruit fly life cycle, we unlock valuable insights into genetics, developmental biology, and disease progression.
These tiny creatures, often seen as common nuisances, have helped shape our understanding of life itself. So, the next time you spot a fruit fly buzzing around your kitchen, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable journey it has undertaken and the knowledge it has contributed to the world of science.

