Seeing a cockroach in your home can be unsettling, but it’s important to have a basic understanding of these creatures when dealing with a potential infestation, such as their lifespan. Cockroach lifespan varies depending on various factors, including their life cycle, environmental conditions, and species. Understanding these factors can help provide insights into their longevity and the implications it has for pest control.
In this article, we will delve into the different stages of the cockroach life cycle, explore the factors that influence their lifespan, examine the lifespan of different cockroach species, discuss the impact of reproduction on their longevity, debunk common misconceptions, look into scientific research on cockroach lifespan, and finally, highlight the implications of cockroach lifespan for pest control strategies.
Understanding the Cockroach Life Cycle
The cockroach life cycle consists of three main stages: the egg stage, the nymph stage, and the adult stage. Each stage plays a crucial role in their overall lifespan and ability to thrive in a given environment.
1. The Egg Stage
The first stage of the cockroach life cycle is the egg stage. Female cockroaches lay eggs in a protective case called an ootheca. Cockroach eggs are typically deposited in warm, dark, and hidden areas, providing a suitable environment for their development. The protective case of the ootheca provides a regulated microenvironment. The ootheca acts as a natural incubator, maintaining the ideal temperature and humidity for the eggs to develop.
Under optimal conditions, cockroach eggs can hatch within a few weeks. However, factors such as temperature and humidity greatly influence their incubation period. Once the eggs hatch, the nymphs emerge, marking the transition to the next stage.
2. The Nymph Stage
During the nymph stage, cockroaches undergo a series of molts as they grow and develop. Nymphs resemble miniature versions of adults but lack fully developed wings and reproductive capabilities. As they molt and shed their exoskeletons, they gradually develop wings and reproductive organs.
The duration of the nymph stage varies depending on factors such as species, environmental conditions, and food availability. Nymphs are highly vulnerable during this stage and require adequate food and shelter to survive and continue their development.
3. The Adult Stage
Once the nymphs reach adulthood, they gain full reproductive capabilities and wings. The lifespan of adult cockroaches can vary significantly, ranging from a few months to several years, depending on various factors.
Adult cockroaches are equipped with wings, which enable them to fly short distances. However, not all species of cockroaches possess fully functional wings, and some are even flightless. The presence or absence of wings is influenced by genetic factors and environmental conditions during the nymph stage.
Adult cockroaches play a vital role in the continuation of their species. They engage in courtship rituals, mate, and lay eggs, starting the life cycle anew. The ability of adult cockroaches to reproduce and ensure the survival of their offspring is crucial for the perpetuation of their species.
Factors Influencing Cockroach Lifespan
The lifespan of cockroaches can be influenced by several factors, primarily revolving around environmental conditions, the availability of food, and the presence of predators and diseases.
Environmental Conditions
A cockroach’s environment plays an essential role in determining their lifespan. Cockroaches thrive in warm and humid conditions, with temperatures between 70 and 90 degrees Fahrenheit (21-32 degrees Celsius) being optimal for survival and reproduction. Extreme temperatures can significantly impact their lifespan. Additionally, humidity levels above 50% create an ideal environment for cockroaches, prolonging their lifespan.
Availability of Food
The availability of food greatly influences cockroach lifespan. Cockroaches are scavengers and can survive on a wide range of organic matter. An ample supply of food sources can increase their chances of survival and reproduction, ultimately leading to a longer lifespan. Conversely, a scarcity of food can result in nutritional deficiencies and shortened lifespans.
Predation and Disease
Predation and disease pose significant threats to cockroach lifespan. Cockroaches have predators such as birds, rodents, and certain reptiles and amphibians. Predation can reduce their overall population and shorten individual lifespans. Additionally, cockroaches are susceptible to various diseases and parasitic infections that can impact their longevity and survival rates.
Lifespan of Different Cockroach Species
Various species of cockroaches exist, each with its distinct characteristics and lifespan. Understanding the lifespan of different species is crucial for effective pest control strategies.
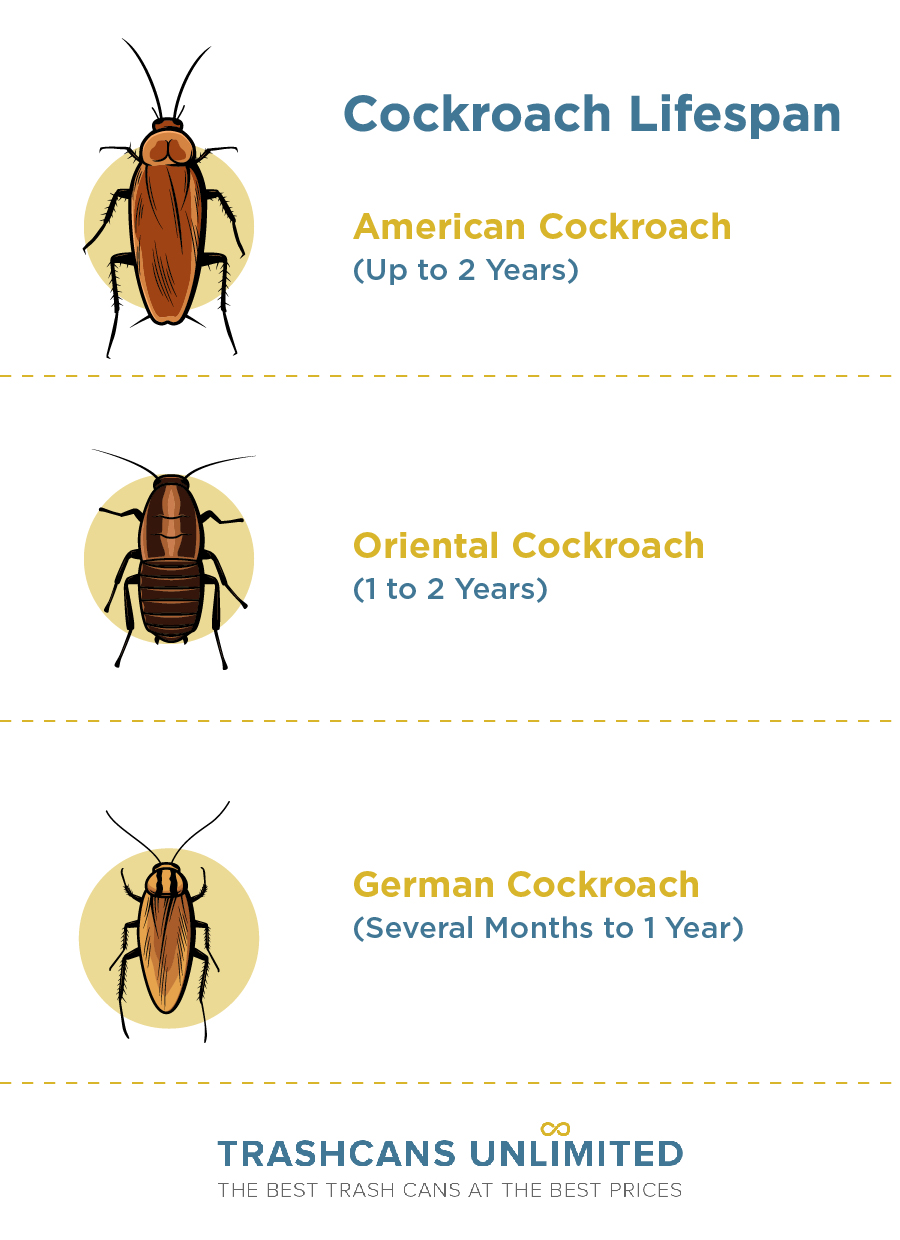
- American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana): This species of cockroach is one of the largest, and with favorable conditions can live up to two years.
- German Cockroach (Blattella germanica): This species is highly adaptable. These cockroaches have a shorter lifespan compared to other species, typically ranging from several months to a year. However, their rapid reproductive capabilities and resilience make them a persistent pest.
- Oriental Cockroach (Blatta orientalis): These cockroaches have a slightly longer lifespan, typically ranging from one to two years. These cockroaches prefer dark, damp environments and are capable of surviving in harsh conditions.
Cockroach Reproduction and Its Impact on Lifespan
Cockroach reproduction plays a significant role in their lifespan. Understanding their reproductive process and the impact it has on population growth is crucial for effective pest control measures.
1. Mating Process
Cockroach mating involves the male depositing a spermatophore, a packet containing sperm, into the female. After mating, the female can produce multiple egg cases, each containing numerous eggs. Mating also triggers changes in the female's behavior and physiology, affecting her longevity.
2. Egg Production and Hatching
Female cockroaches can produce several ootheca throughout their lifespan, each containing viable eggs. The number of ootheca produced depends on various factors, including species, environmental conditions, and food availability. Once the eggs hatch, the nymphs enter the next stage of the life cycle.
Common Misconceptions About Cockroach Lifespan
Several misconceptions about cockroach lifespan exist, often fueled by myths and urban legends. It is essential to debunk these misconceptions to gain a more accurate understanding of their lifespan.
| Myth | Truth |
| Cockroaches can survive extreme levels of radiation, meaning they are nearly invincible creatures. | While cockroaches have shown relative resistance to radiation compared to humans and some other organisms, they are not impervious to it and would succumb to extreme levels of radiation, as do most living organisms. |
| Cockroaches can survive extended periods without food and water. | While cockroaches are known for their ability to survive under harsh conditions, they require a source of nourishment and moisture to thrive and reproduce. Without access to food and water, their lifespan can be significantly shortened. |
Scientific Research on Cockroach Lifespan
Scientific research on cockroach lifespan spans various areas, from studying genetic factors to the impact of pesticides on their longevity. Some particularly interesting areas of study are:
- Genetic Factors: Genetic studies have provided insights into the mechanisms that regulate aging and longevity in cockroaches. Understanding these genetic factors could potentially lead to the development of more targeted pest control methods.
- Impact of Pesticides: Pesticides, when used inappropriately, can contribute to the development of pesticide resistance, potentially reducing their effectiveness in pest control measures. Research aims to find a balance between effective pest control and minimizing negative consequences on cockroach lifespan and the environment.
Implications of Cockroach Lifespan for Pest Control
The lifespan of cockroaches has significant implications for pest control strategies. Understanding their longevity and the factors that influence it can guide the development of effective pest management techniques.
Lifespan and Pest Control Strategies
Cockroaches' ability to adapt and reproduce rapidly presents challenges for extermination efforts. Short lifespan means that targeted control measures must be implemented consistently and persistently to achieve long-term success.
Developing pest control strategies that consider cockroach lifespan can lead to more sustainable and efficient control measures. By targeting specific life cycle stages, such as disrupting reproduction or controlling nymph populations, pest control professionals can make a significant impact on reducing cockroach infestations.
The Intersection of Cockroach Lifespan and Pest Control Options
Cockroach lifespan is influenced by various factors, including their life cycle, environmental conditions, and species' characteristics. Understanding these factors can help inform more effective pest control strategies. By focusing on disrupting their life cycle, creating inhospitable environmental conditions, and implementing targeted control measures, the battle against cockroach infestations can be better waged.

