Originally posted on 7th Mar 2025
The cockroach you spotted last night wasn't alone. If she was a German cockroach—the species infesting most American homes—she's already carrying 30-48 eggs that will hatch in less than a month. German cockroaches develop egg cases 11-12 days after becoming adults and carry them for about three weeks before hatching.¹ American cockroaches produce egg cases every 4 days when mated, or every 10 days when unmated.² A single pregnant female entering your home in January becomes a colony of 30,000 by Christmas. This isn't pest control propaganda; it's mathematical certainty based on their relentless reproductive cycle.
But here's what matters more than the horror: you have a narrow window—about three weeks—before a minor problem explodes into a professional extermination job costing $100-$600.³ This guide arms you with the exact reproduction timelines, early warning signs, and the critical actions that can stop a cockroach infestation before it starts.
Key Takeaways
- German cockroaches produce egg cases every 20-30 days, carrying 30-48 eggs that hatch with 80-90% success rates.
- American cockroaches lay egg cases every 4-10 days (depending on mating status), containing 14-16 eggs each.
- Temperature matters: At 86°F, German roaches hatch in 28 days; at 70°F, it takes 60 days.
- One female = thousands: A single German cockroach female can produce 30,000 descendants in 12 months.
- 3-week window: Early intervention within 21 days achieves 95% success with DIY methods.
- IGR treatments break reproductive cycles but require reapplication every 30-90 days.
- Professional treatment costs $100-$600 depending on infestation severity.
Cockroach Egg-Laying Frequency by Species
Before diving into the science that explains why your skin is crawling, here's exactly how often cockroaches lay eggs and what each species' reproduction means:
|
Species |
Egg-Laying Frequency |
Eggs per Case |
Time to Maturity |
What This Means for Your Home |
|
German |
Every 20-30 days⁴ |
30-40¹ |
54-60 days |
One female = 400 babies in 6 months |
|
American |
Every 4-10 days² |
14-16 |
45-60 days |
Slower spread but harder to eliminate |
|
Oriental |
Every 30-60 days |
16-18 |
60-81 days |
Thrives in basements and cool areas |
|
Brownbanded |
Every 20-25 days |
10-18 |
50-55 days |
Hides oothecae in furniture and electronics |
The German cockroach dominates indoor infestations because of a devastating reproductive advantage: she carries her egg case (ootheca) for the entire development period, protecting it from pesticides, predators, and your desperate attempts at DIY control.
Understanding Cockroach Reproduction
What Are Oothecae and Why They Matter
The brown, pill-shaped capsule you might find behind your refrigerator isn't just an egg case—it's a biological fortress. Each ootheca contains two parallel rows of eggs encased in a protein shell that hardens into chemical-resistant armor. Picture a submarine designed to survive nuclear winter, except it's hiding in your kitchen and contains up to 48 future cockroaches.
German cockroach oothecae look like tiny brown purses measuring 3mm wide by 8mm long with visible segments—each segment contains two eggs, with 30-40 eggs total per case.¹ American cockroach cases stretch longer, colored deep mahogany like expensive leather. Appearance matters less than function: these cases resist most consumer-grade pesticides. In field tests, oothecae survive direct spray applications that kill every adult roach in sight.
The most disturbing detail? Female cockroaches can store sperm for life after mating once. That single encounter fuels months of egg production. Some American cockroaches even reproduce through parthenogenesis—creating viable eggs without any male involvement, a process called automixis-type thelytoky.⁵
The Reproductive Cycle Explained
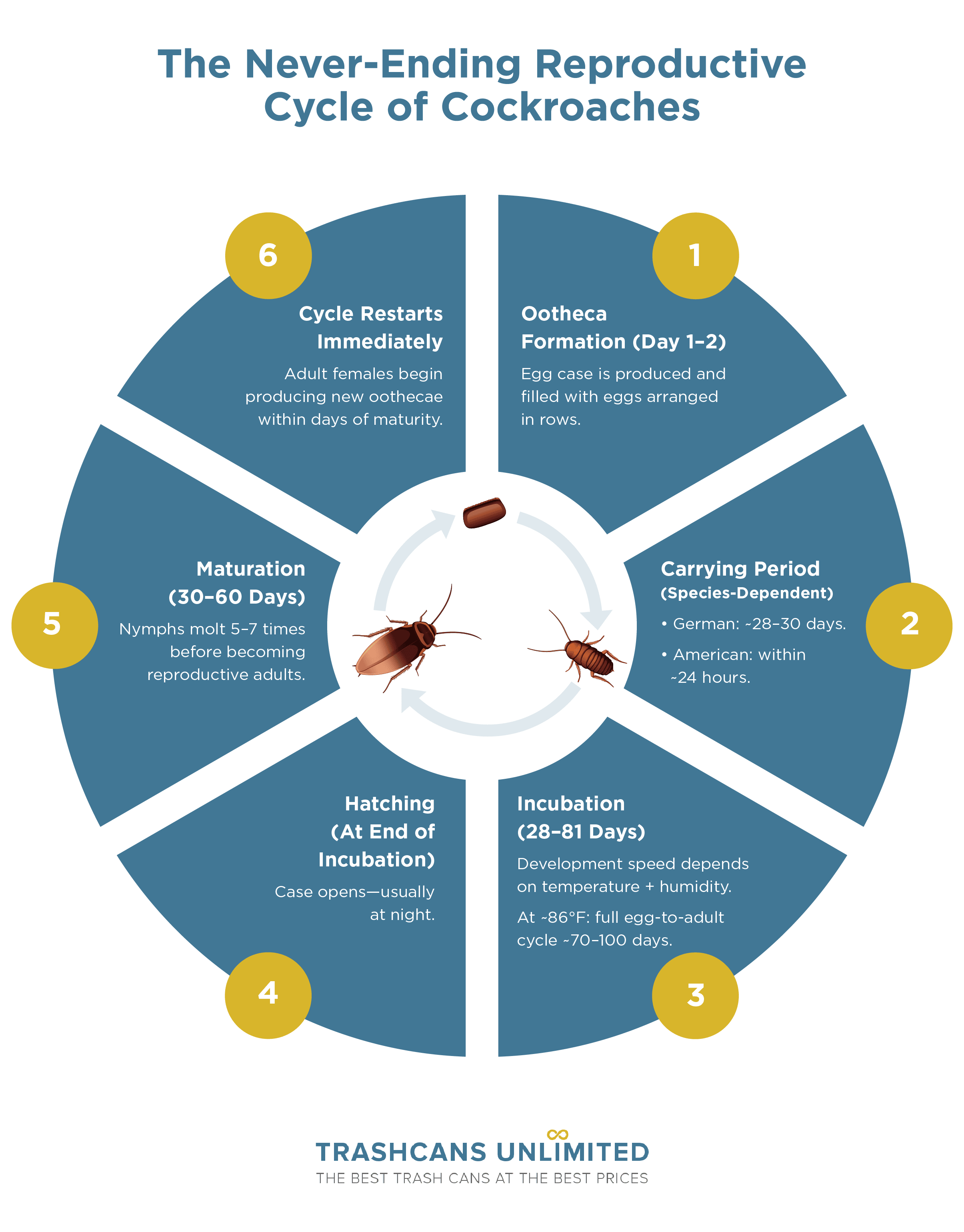
The cycle begins with a brief courtship that would horrify romance novelists. After mating (often just once in her lifetime), the female begins producing oothecae within 24-48 hours. Here's where species diverge dramatically:
- Ootheca Formation (Day 1-2): The female secretes the case from specialized glands, gradually filling it with eggs arranged in precise rows.
- The Carrying Period (Varies by species): German cockroaches carry their cases for 28-30 days until hours before hatching. American cockroaches glue theirs to hidden surfaces within 24 hours.
- Incubation (28-81 days): Temperature and humidity determine development speed. At optimal conditions (86°F with 70% humidity), German cockroach development from egg to adult takes 70-100 days total.⁶
- Hatching: Nymphs emerge en masse, typically at night. A successful German cockroach hatch releases 30-48 tiny white nymphs that darken within hours.
- Maturation (30-60 days): Nymphs molt 5-7 times before reaching reproductive maturity.
- Immediate Restart: Adult females begin producing new oothecae within days of reaching maturity. The cycle never pauses.
Species-Specific Egg-Laying Patterns
German Cockroaches: The Rapid Reproducers
The German cockroach earned its reputation as the ultimate household invader through reproductive efficiency that borders on mathematical perfection. A female develops her first ootheca about 11-12 days after becoming an adult, then produces 5-8 oothecae during her lifetime.¹
By carrying her egg case until hours before hatching, the German cockroach protects the eggs from certain classes of predation and achieves exceptional hatch rates.⁷ This maternal investment means spotting one pregnant female equals finding 40 future roaches, guaranteed.
In apartment buildings, German cockroaches exploit shared plumbing like highways between units. A single pregnant female traveling through bathroom pipes establishes satellite colonies in neighboring apartments within two reproductive cycles—roughly 40-60 days. Property managers report infestations spreading three floors vertically and two units horizontally from a single source apartment within one season.
Under optimal conditions (your heated home in winter), field populations consist of 80% nymphs and 20% adults, demonstrating the constant reproduction occurring.⁸ This isn't theoretical—it's documented in laboratory conditions that mirror modern climate-controlled homes.
American Cockroaches: The Persistent Breeders
American cockroaches compensate for smaller broods with relentless egg production. Research shows mated females produce oothecae every 4 days, while unmated females produce them every 10 days.²
While each ootheca contains only 14-16 eggs, females live 14-15 months and produce 9-10 oothecae on average, though some can produce up to 90.⁹ They prefer commercial buildings, sewers, and basements where stable temperatures support year-round breeding.
Temperature dependency limits American cockroach spread. Below 70°F, reproduction nearly stops. Global warming and modern heating systems increasingly eliminate these natural barriers. Cities report American cockroach populations moving northward, establishing in regions previously too cold for sustained breeding.
Oriental Cockroaches: The Cold-Tolerant Reproducers
Oriental cockroaches shatter the myth that cold climates prevent roach infestations. These black, beetle-like roaches breed successfully at temperatures that halt other species. Females produce oothecae every 30-60 days, depositing them in cool, damp locations like crawl spaces and basement floor drains.
Their slower reproduction rate masks unusual resilience. Oriental cockroach oothecae survive near-freezing temperatures that kill adults. Spring brings synchronized hatching of overwintered egg cases, creating sudden population explosions that overwhelm unprepared homeowners.
Northern cities report increasing Oriental cockroach problems as these cold-adapted breeders exploit heating system fluctuations that would stress other species. They're particularly problematic in older buildings with stone foundations that maintain stable, cool temperatures year-round.
Brownbanded Cockroaches: The High-Place Breeders
Brownbanded cockroaches broke the rules of roach behavior. While other species cluster near water sources, these adaptable invaders thrive in dry conditions and deposit oothecae in locations that conventional treatments miss entirely.
Females glue their cases inside electronics, behind picture frames, under furniture, and inside closets—anywhere except the kitchen and bathroom zones where homeowners typically focus treatment. Each female produces an ootheca every 20-25 days, containing 10-18 eggs that develop faster in warm, dry conditions that would dehydrate other species.
Their reproduction strategy creates treatment nightmares. One female might deposit oothecae in six different rooms, establishing multiple independent colonies. Standard kitchen-focused treatments miss 70% of brownbanded populations hiding in bedrooms and living areas.
Key Environmental Factors That Accelerate Reproduction
The Temperature Sweet Spot (75-85°F)
Your comfortable home creates a cockroach breeding paradise. At 75-85°F—standard indoor temperature—cockroaches achieve optimal reproduction rates. Every 10°F increase above 70°F roughly doubles their breeding speed until hitting thermal maximum at 95°F.
Consider the German cockroach: development takes 70-100 days total from egg to adult under optimal conditions.⁶ This temperature sensitivity explains why summer months bring infestation explosions and why heated buildings support year-round breeding even in frozen climates.
Modern HVAC systems eliminated seasonal reproduction breaks. Your consistent 72°F home provides uninterrupted breeding conditions that wild roach populations never experienced. Climate-controlled buildings transformed occasional invaders into permanent residents.
Humidity: The Hidden Accelerator
Bathroom infestations reveal humidity's critical role. At 60-80% humidity—typical for bathrooms during and after showers—cockroach eggs achieve maximum hatch rates. Drop humidity below 40%, and ootheca desiccation reduces hatching significantly.
Kitchens compound the problem. Dishwashers create micro-climates of 90% humidity during cycles. Under-sink cabinets trap moisture from minor leaks. Even coffee makers generate enough localized humidity to support cockroach breeding beneath them.
Research demonstrates that group-housed female cockroaches even promote asexual ootheca production when together—colonies maintained by fifteen females have survived over three years through parthenogenesis alone.¹⁰
Food Sources That Support Maximum Breeding
Cockroaches breed faster with protein access. Pet food left overnight, grease films behind stoves, and organic garbage provide optimal nutrition for egg production. One study found females with protein access produce 40% more oothecae than those limited to carbohydrates.
Modern homes offer buffets of micro-foods: toaster crumb trays, garbage disposal splash zones, pet food dust, and cooking oil residues coating exhaust fans. Each overlooked source supports additional breeding pairs.
The Dark and Hidden Spaces Requirement
Cockroaches require harborage matching their body size. German cockroaches prefer 3/8-inch cracks—credit card width. American cockroaches need 1/2-inch spaces. Without proper hiding spots, stress hormones suppress reproduction.
Modern construction creates ideal breeding architecture. Hollow cabinet kickplates, gaps behind dishwashers, spaces between walls and cabinets—each provides darkness, warmth, and protection. One apartment building study found 89% of the population concentrated within 10 feet of water sources, but breeding occurred throughout units wherever darkness and crevices aligned.
The Multiplication Timeline: From One Roach to Thousands
Month 1: The Silent Invasion
A single fertilized female German cockroach enters through a grocery bag. She's already carrying her first ootheca—30-40 eggs developing inside the protective case. She locates the void beneath your dishwasher: warm, humid, dark, with nearby food residue. Perfect.
Within days, she identifies water sources: the dishwasher door seal's minor leak, condensation beneath the sink, pet water bowl 20 feet away. She feeds nocturnally on invisible grease films and microscopic food particles.
Meanwhile, the eggs develop. Protected by her body, they're immune to surface sprays, temperature fluctuations, and desiccation. After about three weeks of carrying, she deposits the case hours before hatching—a critical moment when most other species' eggs face maximum vulnerability, but German cockroach young emerge protected by maternal timing.
Population: 2 adults, 30-40 developing eggs.
Month 2-3: The Multiplication Point
The first ootheca hatches, releasing 35 nymphs. These tiny, white insects darken within hours and begin their first molt within days. The original female deposits her third and fourth oothecae while the male finds and fertilizes a newly matured female from a neighboring apartment.
This marks your last chance for easy intervention. Seeing one roach during evening hours signals the population has reached 50-100 individuals. Miss this window, and exponential growth becomes inevitable.
Population: 100-150 roaches across multiple life stages.
Month 4-6: The Explosion
First-generation nymphs reach maturity and begin breeding. Multiple females now produce oothecae simultaneously. The colony fragments, establishing satellite populations in adjoining rooms. Roaches appear during daylight—a desperate sign of overcrowding.
Professional exterminators recognize this phase immediately. Day-active roaches indicate the population exceeds available hiding spaces. For every visible roach, 50-100 remain hidden. The mathematical progression becomes terrifying: each breeding female from month 2 now produces her own offspring.
Population: 500-1,000+ roaches, structural infestation established.
Breaking the Reproductive Cycle: Proven Strategies
Immediate Actions (First 24 Hours)
The moment you spot evidence of cockroaches, these five actions can prevent establishment:
- Eliminate water completely: Fix drips, dry all sinks, remove pet water overnight. Cockroaches survive weeks without food but only days without water.
- Deep clean with purpose: Pull out appliances and clean beneath—don't just wipe counters. Vacuum crevices where eggs hide. Empty toasters, clean disposal splash zones.
- Seal entry points now: Steel wool pushed into gaps provides immediate barriers roaches can't chew through. Follow with caulk for permanence.
- Deploy glue traps strategically: Place along walls every 10 feet to assess population size and identify traffic patterns.
- Remove cardboard immediately: Roaches preferentially breed in corrugated cardboard's warm, humid channels.
Targeted Treatment Approaches
Modern cockroach control centers on IGRs—Insect Growth Regulators that break reproductive cycles without killing adults. Hydroprene and pyriproxyfen work by preventing nymphs that have been exposed from ever molting into adults or developing into sterile adults that cannot reproduce.¹¹
Bait placement follows roach behavior patterns. Roaches travel edges, so place bait stations every 10 linear feet along kitchen walls, every 15 feet elsewhere. Corner placement achieves better contact rates than open areas. Combine IGR stations with traditional gel baits for dual action—killing current adults while preventing future reproduction.
Critical detail most homeowners miss: IGRs typically remain effective for about 30 days when used for indoor treatments. Mark calendars for reapplication or face population rebounds. Professional-grade IGRs last longer but require applicator licenses in most states.
Long-term Prevention Protocol
Sustainable roach prevention requires systematic vigilance:
- Weekly: Deep clean focusing on overlooked food sources. Move appliances monthly to clean beneath.
- Bi-weekly: Inspect perimeter for new entry points. Check under-sink areas for moisture.
- Monthly: Replace bait stations and IGR treatments. Document any sightings with location and time.
- Quarterly: Professional inspection of hidden areas—wall voids, drop ceilings, behind built-in appliances.
IGRs are more selective and environmentally compatible with integrated pest management (IPM) systems that include biological control.¹²
When to Call Professionals
Signs You're Past DIY Solutions
Industry thresholds for professional intervention:
- 5+ roaches seen in daylight: Indicates 100-500 hidden individuals
- Fresh oothecae weekly: Active, expanding breeding population
- Presence in 3+ rooms: Established satellite colonies requiring structural treatment
- DIY failure after 30 days: Developing pesticide resistance or missed harborage sites
The mathematical reality: Early intervention (first 30 days) achieves 95% success with consumer methods. After three months, even professional success rates drop to 70% without structural fumigation.
What Professional Treatment Includes
Modern professional treatments exploit reproductive vulnerabilities:
- Advanced IGR applications: Commercial-grade formulations last 120+ days
- Void treatments: Injecting inside walls where colonies establish
- Crack and crevice precision: Targeting ootheca deposit sites
- Follow-up monitoring: Quarterly inspections to catch reinfestations early
- Warranty programs: Retreatment guarantees if populations return
Professional extermination costs range from $100-$400 for minor infestations to $300-$700 per treatment for major infestations.³
Your Action Plan
The cockroach you saw represents a ticking mathematical bomb. German cockroaches developing egg cases every few weeks become thousands within months. American cockroaches producing cases every 4-10 days establish permanent colonies. You're not helpless against these numbers.
Tonight: Remove every water source. Fix that drip, dry those dishes, empty that pet bowl.
Tomorrow: Apply IGR-containing baits in strategic locations along walls and corners.
This week: Seal entry points with steel wool and caulk, creating physical barriers against reinforcement.
A single pregnant cockroach becomes 30,000 descendants within one year, but early action stops the multiplication cold. The three-week window after first sighting determines whether you face a minor inconvenience or major infestation.
Understanding cockroach reproduction timelines transforms panic into power. German cockroaches producing egg cases every 20-30 days, American species every 4-10 days—these aren't just statistics, they're your battle rhythm. Temperature and humidity control, strategic IGR deployment, and vigilant monitoring break the reproductive cycle before exponential growth begins. The difference between a $20 DIY solution and a $700 professional intervention is measured in weeks, not months. Act within that critical three-week window, and you control the outcome. Wait, and mathematics controls you.
Don't let waste management become your weakest link. Secure your home's first line of defense with pest-proof waste management solutions at Trashcans Unlimited.
References
- University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. "The German Cockroach." EDIS, University of Florida IFAS Extension, 22 Feb. 2022, https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/IN028
- Lin, Liangguan, et al. "Life-History Traits from Embryonic Development to Reproduction in the American Cockroach." Insects, vol. 13, no. 6, 2022, article 551, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9225176/
- "How Much Do Cockroach Exterminators Cost? [2025 Data]." Angi, 24 Sep. 2025, https://www.angi.com/articles/how-much-does-cockroach-extermination-cost.htm
- "Differential physiological responses of the German cockroach to social interactions during the ovarian cycle." Journal of Experimental Biology, 01 Sep. 2012, https://journals.biologists.com/jeb/article/215/17/3037/11001/Differential-physiological-responses-of-the-German
- Tanaka, Masashi, et al. "First molecular genetic evidence for automictic parthenogenesis in cockroaches." Insect Science, vol. 26, no. 4, 2019, pp. 649-658, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29389065/
- "Biology and Behavior of the German Cockroach." NC State Extension Publications, https://content.ces.ncsu.edu/biology-behavior-of-the-german-cockroach
- "German cockroach." Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_cockroach
- "FS1322: German Cockroach." Rutgers New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station, Rutgers University, https://njaes.rutgers.edu/fs1322/
- "American cockroach." Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_cockroach
- Katoh, Ko, et al. "Group-housed females promote production of asexual ootheca in American cockroaches." Zoological Letters, vol. 3, 13 Mar. 2017, https://zoologicalletters.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40851-017-0063-x
- "How Do Insect Growth Regulators Work?" Pest Control Technology, 19 June 2025, https://www.pctonline.com/article/pct0112-insect-growth-regulators/
- "Insect Growth Regulators." WSU Tree Fruit, Washington State University, https://treefruit.wsu.edu/crop-protection/opm/igrs/

